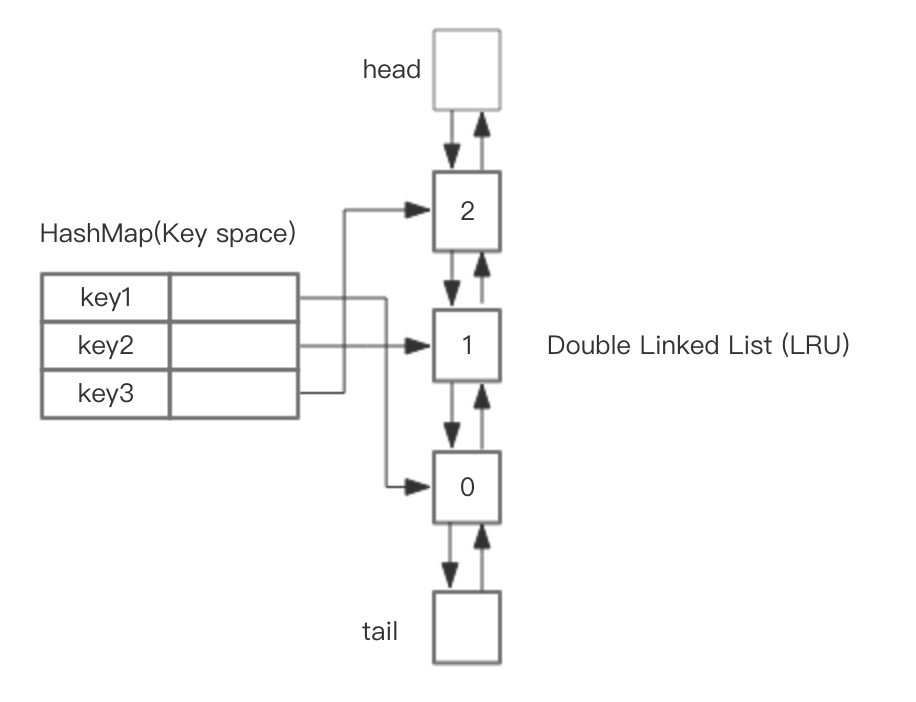
LRU 队列实现
146. LRU 缓存机制
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制。它应该支持以下操作: 获取数据 get 和 写入数据 put 。
获取数据 get(key) - 如果密钥 (key) 存在于缓存中,则获取密钥的值(总是正数),否则返回 -1。
写入数据 put(key, value) - 如果密钥不存在,则写入其数据值。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最近最少使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
进阶:
你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?
示例:
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache( 2 /* 缓存容量 */ );
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.get(1); // 返回 1
cache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得密钥 2 作废
cache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
cache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得密钥 1 作废
cache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
cache.get(3); // 返回 3
cache.get(4); // 返回 4
解法一
改了好几次才改对,核心思路就是利用 HashMap+双向链表
public class LRUCache {
class Node{
int key;
int value;
Node pre;
Node next;
public Node(int key,int value){
this.value=value;
this.key=key;
}
}
HashMap<Integer,Node> map=new HashMap<>();
Node head=null;
Node tail=null;
int capacity=0;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity=capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
Node node=map.get(key);
//移动到链表头
move2Head(node);
return node.value;
}
return -1;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
Node newHead=new Node(key,value);
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
Node node=map.get(key);
node.value=value;
//移动到链表头
move2Head(node);
return;
}
if (map.size()==capacity) {
map.remove(tail.key);
removeNode(tail);
}
move2Head(newHead);
map.put(key,newHead);
}
public void removeNode(Node node){
if (node.key==tail.key) {
tail=tail.pre;
return;
}
if (node.pre==null || node.next==null) {
return;
}
node.pre.next=node.next;
node.next.pre=node.pre;
}
public void move2Head(Node newHead){
if (map.size()==0) {
head=tail=newHead;
return;
}
if (newHead.key==head.key) {
return;
}
removeNode(newHead);
newHead.next=head;
newHead.pre=null;
head.pre=newHead;
head=newHead;
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/
既然已经实现了,我们就来考虑下为啥要这样实现
其实我一开始也不知道咋实现,查了下才知道,这里有几个点需要注意:
-
首先是题目要求 get/put 时间复杂度是
O(1)的,而我们在 get/put 的时候肯定会频繁的移动元素的位置,那我们肯定是不能用数组,队列之类的结构了 -
那我们能用单链表么?我们可以将最近访问的节点放在头部,然后每次满的时候剔除尾节点的元素,由于是链表,移动节点的位置都是很容易的,但是我们如果要 get 一个元素的时候就麻烦了,需要遍历整个链表才能取到元素,也就是说单链表定位某个元素比较耗时,所以我们考虑用 HashMap 来辅助单链表,这样我们以 key 为 map 的 key,Node 节点为 map 的 value 就可以迅速定位到某个元素
-
单链表+HashMap 就可以了么?其实还差点儿,如果现在满了,需要删除最后一个节点,那我们就需要将 tail 的前一个作为新的 tail,但是由于是单链表,没有前置指针,不方便定位前一个节点,所以我们最后的方案就是采用**双向链表+HashMap **来实现 LRU

其实 LRU 思想并不复杂,按照规则来移动节点,删除节点就 OK,操作系统教程上也有类似的过程图,理解了下面的图代码就好写了

但是如果实现的方式不太好的话,就会写很多 if-else 判断一些边界,比如我上面自己的实现就是。
其实还有一个原因就是我上面的方式 head 和 tail 是真实的节点,不是虚节点,所以会有很多边界的逻辑判断,面试的时候不建议那样写,很容易出问题!!!
解法二
面试中比较推荐像这样写
public class LRUCache {
class Node{
int key;
int value;
Node pre;
Node next;
public Node(int key,int value){
this.value=value;
this.key=key;
}
}
HashMap<Integer,Node> map=new HashMap<>();
Node head=null;
Node tail=null;
int capacity=0;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity=capacity;
//初始化头尾节点,注意这两个节点只是个哨兵节点,并不会存入 map 中
head=new Node(-1,-1);
tail=new Node(-1,-1);
head.next=tail;
tail.pre=head;
}
public int get(int key) {
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
Node node=map.get(key);
//移动到链表头
move2Head(node);
return node.value;
}
return -1;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
Node newHead=new Node(key,value);
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
Node node=map.get(key);
//设置节点值为新 value
node.value=value;
//移动到链表头
move2Head(node);
return;
}
//满了,先剔除 tail 再插入
if (map.size()==capacity) {
map.remove(popTail().key);
}
addFirst(newHead);
map.put(key,newHead);
}
//弹出 tail
private Node popTail(){
Node newTail=tail.pre;
removeNode(newTail);
return newTail;
}
//移除节点
private void removeNode(Node node){
node.pre.next=node.next;
node.next.pre=node.pre;
}
//从头添加
private void addFirst(Node node){
node.next=head.next;
head.next.pre=node;
head.next=node;
node.pre=head;
}
//移动节点到 head
private void move2Head(Node node){
//删除原链表中对应位置的 node
removeNode(node);
//从头再添加一遍
addFirst(node);
}
}
像这样写,就不用考虑那么多边界,写那么多的 if 和 else,预先开辟两个节点的作为哨兵节点,这样代码就显得清晰简洁,也不容易出问题
UPDATE
随便重写了下
class LRUCache {
HashMap<Integer, Node> map = null;
int capacity = 0;
Node head = null;
Node tail = null;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
map = new HashMap<>();
head = new Node(-1, -1);
tail = new Node(-1, -1);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
Node node = map.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return -1;
}
removeNode(node);
insert2head(node);
return node.val;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
Node node = map.get(key);
if (node == null) {
node = new Node(key, value);
insert2head(node);
map.put(key, node);
} else {
removeNode(node);
node.val = value;
insert2head(node);
}
if (map.size() > capacity) {
map.remove(tail.prev.key);
removeNode(tail.prev);
}
}
public void insert2head(Node node) {
node.next = head.next;
node.prev = head;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
//移除 Node 节点
public void removeNode(Node node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
node.next = null;
node.prev = null;
}
class Node {
Node prev, next;
int key, val;
public Node (int key, int val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/
Golang
type LRUCache struct {
capacity int
cache map[int]*Node
head *Node
tail *Node
}
type Node struct {
prev *Node
next *Node
key int
val int
}
func Constructor(capacity int) LRUCache {
head := &Node{key : -1, val : -1}
tail := &Node{key : -1, val : -1}
head.next = tail
tail.next = head
return LRUCache{
capacity : capacity,
cache : make(map[int]*Node),
head : head,
tail : tail,
}
}
func (this *LRUCache) Get(key int) int {
if v, ok := this.cache[key]; ok {
this.removeNode(v)
this.insert2Head(v)
return v.val
}
return -1
}
func (this *LRUCache) Put(key int, value int) {
if v, ok := this.cache[key]; ok {
this.removeNode(v)
v.val = value
this.insert2Head(v)
} else {
newNode := &Node{key : key, val : value}
this.cache[key] = newNode
this.insert2Head(newNode)
}
if len(this.cache) > this.capacity {
delete(this.cache, this.tail.prev.key)
this.removeNode(this.tail.prev)
}
}
func (this *LRUCache) removeNode (node *Node) {
node.next.prev = node.prev
node.prev.next = node.next
node.prev = nil
node.next = nil
}
func (this *LRUCache) insert2Head (node *Node) {
node.prev = this.head
node.next = this.head.next
this.head.next.prev = node
this.head.next = node
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor(capacity);
* param_1 := obj.Get(key);
* obj.Put(key,value);
*/