AtCoder Beginner Contest 190
比赛地址: https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc190
完整代码(A-F):Github
A - Very Very Primitive Game
先下手的人 candies 数量 大于 另一个人就能赢
B - Magic 3
循环判断
C - Bowls and Dishes
We have $N$ dishes numbered $1, 2, \dots, N$ and $M$ conditions numbered $1, 2, \dots, M$ .
Condition $i$ is satisfied when both Dish $A_i$ and Dish $B_i$ have (one or more) balls on them.
There are $K$ people numbered $1, 2, \dots, K$ . Person $i$ will put a ball on Dish $C_i$ or Dish $D_i$ . At most how many conditions will be satisfied?
Constraints
- All values in input are integers.
- $2 ≤ N ≤ 100$
- $1 ≤ M ≤ 100$
- $1 ≤ A_i < B_i ≤ N$
- $1 ≤ K ≤ 16$
- $1 ≤ C_i < D_i ≤ N$
Sample Input 1
4 4
1 2
1 3
2 4
3 4
3
1 2
1 3
2 3
Sample Output 1
2
解法一
题目大意:有 $N$ 个空盘子,然后给定 $M$ 个询问,如果 $Ai$ -th 和 $Bi$ -th 的盘子(从 1 开始)上都有至少一个球,那么这个询问就满足了,然后给了 $K$ 给选择,每个选择可以从两个盘子中选一个盘子然后将一个球放到其中,问最多能满足多少个询问
这个题比赛的时候也卡了一会儿,最后算了下暴力的复杂度,发现直接暴力枚举就行了。枚举所有的放置情况,然后求一个最大值就行了,时间复杂度 $O(2^K*M)$
//比赛时的 code,太丑了
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
static int[] dish;
static int[][] w;
static int[][] kn;
static int K;
static int N, M;
static int res = 0;
//2^16*100 = 1024 * 100 * 100 = 1000 0000
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int[] in = read(br);
N = in[0]; M = in[1];
dish = new int[N];
w = new int[M][2];
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
w[i][0] = t[0]; w[i][1] = t[1];
}
K = read(br)[0];
kn = new int[K][2];
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
kn[i][0] = t[0]; kn[i][1] = t[1];
}
dfs(0);
out.println(res);
out.flush();
}
public static void dfs(int i) {
if (i == K) {
res = Math.max(res, check());
return;
}
dish[kn[i][0]-1]++;
dfs(i+1);
dish[kn[i][0]-1]--;
dish[kn[i][1]-1]++;
dfs(i+1);
dish[kn[i][1]-1]--;
}
public static int check() {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
if (dish[w[i][0]-1] >= 1 && dish[w[i][1]-1] >= 1) {
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
解法二
二进制枚举,赛后独立写出来的,时间复杂度 $O(2^K(K+M))$
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
//2^16*100 = 1024 * 100 * 100 = 1000 0000
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int[] in = read(br);
int N = in[0], M = in[1];
int[][] cond = new int[M][2];
//注意输入都是从 1 开始的
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
cond[i] = new int[]{t[0]-1, t[1]-1};
}
int K = read(br)[0];
int[][] kn = new int[K][2];
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
kn[i] = new int[]{t[0]-1, t[1]-1};
}
int res = 0;
//000 001 011
for (int i = 0; i < (1<<K); i++) {
int[] dish = new int[N];
for (int j = 0; j < K; j++) {
//这里不用考虑无符号右移
dish[kn[K-1-j][(i>>j)&1]]++;
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (dish[cond[j][0]] >= 1 && dish[cond[j][1]] >= 1) {
cnt++;
}
}
res = Math.max(res, cnt);
}
out.println(res);
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
D - Staircase Sequences
How many arithmetic progressions consisting of integers with a common difference of $1$ have a sum of $N$ ?
Constraints
- $1≤N≤10^12$
- $N$ is an integer.
Sample Input 1
12
Sample Output 1
4
We have four such progressions:
- $[12]$
- $[3, 4, 5]$
- $[-2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]$
- $[-11, -10, -9, \dots, 10, 11, 12]$
解法一
公差是 $1$ 的等差数列前 $n$ 项和: $S= \frac{(a_0+a_0+n-1)n}{2}$ ,转换一下就变成了 $\frac{2S}{n}+1-n=2a_0$ ,那么首先 $n$ 肯定是整数,其次题目说了 $a_i$ 也是整数,所以上述式子需要保证这两个条件,那么我们直接枚举 $2N$ 的因子 $f$ ,然后判断 $\frac{2S}{f}+1-f$ 是否是偶数就行了,时间复杂度 $O(\sqrt{N})$ (看题目数据范围 $1e12$ 就知道肯定是根号的复杂度)
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
long N = Long.valueOf(br.readLine());
// (a+a+n-1)*n/2 = N ==> 2a = 2N/n + 1 - n
// 枚举 2N 的所有因子
long x = 2*N;
HashSet<Long> set = new HashSet<>();
//i*i 大于 x 那么 i 之前肯定已经被加入了
for (long i = 1; i*i <= x; i++) {
if ((x%i) == 0) {
set.add(i);
set.add(x/i);
}
}
long res = 0;
for (Long f : set) {
if ((x/f+1-f)%2==0) res++;
}
out.println(res);
out.flush();
}
}
E - Magical Ornament
There are $N$ kinds of magical gems, numbered $1, 2, \ldots, N$ , distributed in the AtCoder Kingdom.
Takahashi is trying to make an ornament by arranging gems in a row.
For some pairs of gems, we can put the two gems next to each other; for other pairs, we cannot. We have $M$ pairs for which the two gems can be adjacent: (Gem $A_1$ , Gem $B_1$ ), (Gem $A_2$ , Gem $B_2$ ), $\ldots$ , (Gem $A_M$ , Gem $B_M$ ). For the other pairs, the two gems cannot be adjacent. (Order does not matter in these pairs.)
Determine whether it is possible to form a sequence of gems that has one or more gems of each of the kinds $C_1, C_2, \dots, C_K$ . If the answer is yes, find the minimum number of stones needed to form such a sequence.
Constraints
- All values in input are integers.
- $1 ≤ N ≤ 10^5$
- $0 ≤ M ≤ 10^5$
- $1 ≤ A_i < B_i ≤ N$
- If $i ≠ j, (A_i, B_i) ≠ (A_j, B_j)$ .
- $1 ≤ K ≤ 17$
- $1 ≤ C_1 < C_2 < \dots < C_K ≤ N$
Sample Input 1
4 3
1 4
2 4
3 4
3
1 2 3
Sample Output 1
5
解法一
bfs+状态压缩,因为 $K$ 很小,所以我们可以将给定的输入转换成一个双向图,然后将关键点之间的最短路径求出来,这里直接 BFS 就行了,时间复杂度 $O(K*(N+M))$ ,得到一个 $dist[i][j]$ ,表示第 $i$ -th 关键点和第 $j$ -th 个关键点的最短路径
然后再进行状态压缩,设置状态为: $dp[mask][last]$ ,选取 $mask$ 代表的 关键宝石,并且以 $last$ 宝石结尾的最短序列长度(显然 $last$ 一定是关键宝石)
- 入口: $dp[1 « i][i] = 1$ ,只选取一个关键宝石,序列长度为 1
- 转移: $dp[mask|(1 « j)][j] = \min(dp[mask][i] + dist[i][j])$ ,枚举所有的选取状态,枚举所有以关键宝石作为结尾的状态,递推求最小值
- 出口: $\min_i(dp[(1 « k)-1][i])$ ,选取到所有的关键石头,并且以某个关键石头结尾的最小值
代码实现如下(注意下标统一,给的输入都是从 1 开始的,需要转换,一开始转换掉了一个,找了半天的 bug):
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int[] in = read(br);
int N = in[0], M = in[1];
int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
List<Integer>[] adj = new ArrayList[N];
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
int x = t[0]-1, y = t[1]-1;
if (adj[x] == null) {
adj[x] = new ArrayList<>();
}
if (adj[y] == null) {
adj[y] = new ArrayList<>();
}
adj[x].add(y); adj[y].add(x);
}
int K = read(br)[0];
int[] C = read(br);
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) map.put(--C[i], i);
//K 个关键点之间的最短距离
int[][] dis = new int[K][K];
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
Arrays.fill(dis[i], INF);
queue.clear();
queue.add(new int[]{C[i], 0});
boolean[] vis = new boolean[N];
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = queue.poll();
if (map.containsKey(cur[0])) {
dis[i][map.get(cur[0])] = cur[1];
}
if (adj[cur[0]] == null) continue;
for (Integer next : adj[cur[0]]) {
if (vis[next]) continue;
queue.add(new int[]{next, cur[1]+1});
vis[next] = true;
}
}
}
int[][] dp = new int[1<<K][K];
for (int i = 0; i < (1<<K); i++) {
Arrays.fill(dp[i], INF);
}
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
dp[1<<i][i] = 1;
}
//枚举所有状态递推
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1<<K); mask++) {
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
//C[i] 被选取,C[j] 未被选取(因为有 INF 的原因,判断去掉也可 AC,不过最好还是加上)
if ((mask&(1<<i))==0) continue;
for (int j = 0; j < K; j++) {
if ((mask&(1<<j))==1 || dis[i][j] == INF || dp[mask][i] == INF) continue;
dp[mask|(1<<j)][j] = Math.min(dp[mask|(1<<j)][j], dp[mask][i] + dis[i][j]);
}
}
}
int res = INF;
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
res = Math.min(res, dp[(1<<K)-1][i]);
}
if (res == INF) out.println(-1);
else out.println(res);
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
F - Shift and Inversions
Given is a sequence $A = [a_0, a_1, a_2, \dots, a_{N-1}]$ that is a permutation of $0, 1, 2, \dots, N - 1$ .
For each $k = 0, 1, 2, \dots, N - 1$ , find the inversion number of the sequence $B = [b_0, b_1, b_2, \dots, b_{N-1}]$ defined as $b_i = a_{i+k \bmod N}$ .
Constraints
- All values in input are integers.
- $2≤N≤3×10^5$
- $a_0,a_1,a_2,…,a_{N−1}$ is a permutation of $0,1,2,…,N−1$ .
Sample Input 1
4
0 1 2 3
Sample Output 1
0
3
4
3
We have $A = [0, 1, 2, 3]$ .
- For $k = 0$ , the inversion number of $B = [0, 1, 2, 3]$ is $0$ .
- For $k = 1$ , the inversion number of $B = [1, 2, 3, 0]$ is $3$ .
- For $k = 2$ , the inversion number of $B = [2, 3, 0, 1]$ is $4$ .
- For $k = 3$ , the inversion number of $B = [3, 0, 1, 2]$ is $3$ .
解法一
首先 $B_{k=i}$ 序列实际上就是 $A$ 数组将开头的 $i$ 个元素移动到后面得到的序列。同时题目说了给定的 $A$ 序列是 $0,1,2 \ldots N-1$ 的一个排列,所以我们把某个元素从开头移动到结尾的逆序对变化是可以直接计算出来的
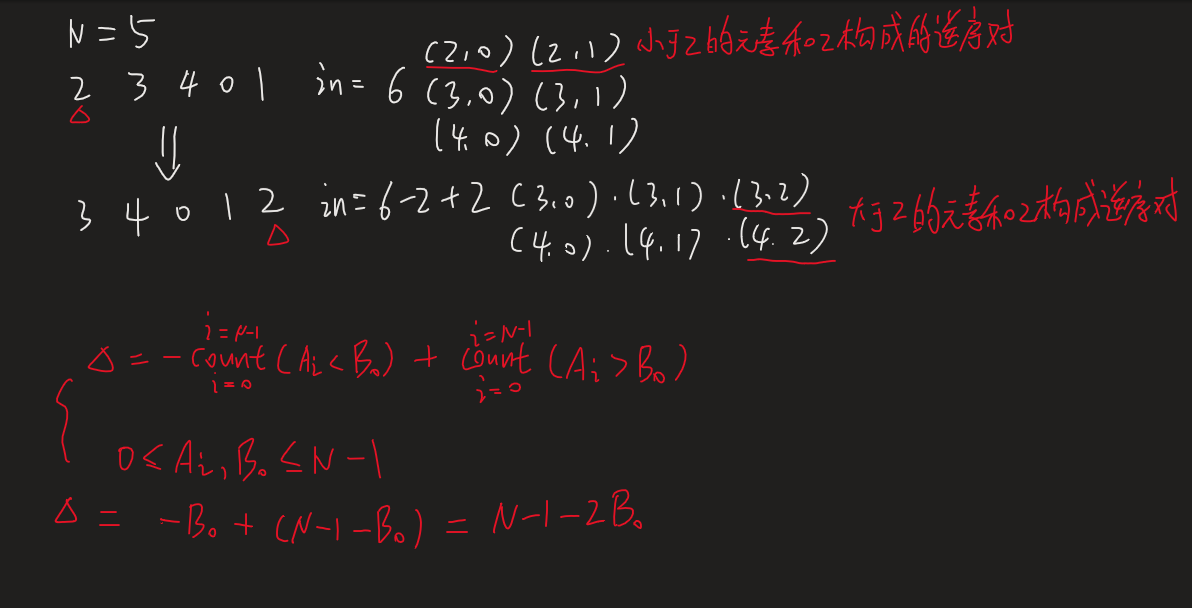 所以我们只需要求出初始 $A$ 数组的逆序对个数然后按照上面的式子递推就行了,这里我采用树状数组的方法求逆序对,也可以用归并排序的方式
所以我们只需要求出初始 $A$ 数组的逆序对个数然后按照上面的式子递推就行了,这里我采用树状数组的方法求逆序对,也可以用归并排序的方式
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
static int[] tree;
public static int lowbit(int x) {
return x & -x;
}
//q[1001] = t[1001] + t[1000]
public static int query(int i) {
int res = 0;
while (i > 0) {
res += tree[i];
i -= lowbit(i);
}
return res;
}
public static void add(int i, int val) {
while (i < tree.length) {
tree[i] += val;
i += lowbit(i);
}
}
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int N = read(br)[0];
int[] A = read(br);
tree = new int[N+1];
//这题不用离散化,序列值就是 Rank
long res = 0;
//树状数组或者归并都可
for (int i = N-1; i >= 0; i--) {
add(A[i]+1, 1);
res += query(A[i]);
}
out.println(res);
//-k+(N-1-k) = N-1-2*k
for (int i = 0; i < N-1; i++) {
res += N-1-2*A[i];
out.println(res);
}
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
一开始写了个假的算法结果 AC 了,主要是离散化写错了(这题本来也不用离散化,写离散化属于我吃饱了撑的,完了还写了个错的,还好,给自己提前暴雷了),幸好我尝试去写了其他的解法,不然这个错误就被混过去了 错误代码 Gist
解法二
进一步的解法,序列的值是完全随机的的做法,这个时候归并就不太行了,而对于树状数组只需要稍微稍微改动一下就行了。
class Main {
static int[] tree;
public static int lowbit(int x) {
return x & -x;
}
//q[1001] = t[1001] + t[1000]
public static int query(int i) {
int res = 0;
while (i > 0) {
res += tree[i];
i -= lowbit(i);
}
return res;
}
public static void add(int i, int val) {
while (i < tree.length) {
tree[i] += val;
i += lowbit(i);
}
}
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int N = read(br)[0];
int[] A = read(br);
tree = new int[N+1];
//离散化(这题不用离散化,为了更加通用)
int[][] temp = new int[N][2];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) temp[i] = new int[]{A[i], i};
Arrays.sort(temp, (t1, t2)->t1[0]-t2[0]);
int[] rank = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
rank[temp[i][1]] = i+1;
}
long res = 0;
//树状数组或者归并都可
for (int i = N-1; i >= 0; i--) {
add(rank[i], 1);
res += query(rank[i]-1);
}
out.println(res);
//改动的地方
for (int i = 0; i < N-1; i++) {
res -= query(rank[i]-1);
res += query(N) - query(rank[i]);
out.println(res);
}
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}