AtCoder Beginner Contest 189
比赛地址:https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc189
完整代码(A-F):Github
A - Slot
直接判断就行了
B - Alcoholic
注意避免用除,转换成乘
C - Mandarin Orange
There are $N$ dishes arranged in a row in front of Takahashi. The $i$ -th dish from the left has $A_i$ oranges on it.
Takahashi will choose a triple of integers $(l, r, x)$ satisfying all of the following conditions:
- $1 \leq l \leq r \leq N$
- $1 \le x$
- for every integer $i$ between $l$ and $r$ (inclusive), $x \le A_i$ .
He will then pick up and eat $x$ oranges from each of the $l$ -th through $r$ -th dishes from the left.
At most how many oranges can he eat by choosing the triple $(l, r, x)$ to maximize this number?
Constraints
- All values in input are integers.
- $1 \leq N \leq 10^4$
- $1 \leq A_i \leq 10^5$
Sample Input 1
6
2 4 4 9 4 9
Sample Output 1
20
解法一
暴力 $O(N^2)$ 的方法,枚举所有区间,以及区间最小值,数据范围 $1e4$ ,在 LC 上肯定超时了,但是在这里好像不仅不会超时,速度还很快,180ms
不过这个题放在这个位置正确的解法应该就是下面的暴力,如果放到 D 题,然后数据范围大一点,就没这么简单了,就是下面的解法二了
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int N = read(br)[0];
int[] w = read(br);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (i > 0 && w[i] == w[i-1]) continue;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = i; j < N; j++) {
min = Math.min(w[j], min);
res = Math.max(res, min*(j-i+1));
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
解法二
单调栈的解法,和 Lc84. 柱状图中最大的矩形 是一道题,时间复杂度 $O(N)$
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
//2 4 4 9 4 9
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int N = read(br)[0];
int[] w = new int[N+1];
System.arraycopy(read(br), 0, w, 0, N);
w[N] = -1;
//单调递增栈
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && w[stack.peek()] > w[i]) {
int cur = stack.pop();
//向左最多扩展到 left+1,向右最多扩展到 i-1 (i-1-left-1+1)
int left = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
res = Math.max(res, (i-1-left)*w[cur]);
}
stack.push(i);
}
System.out.println(res);
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
D - Logical Expression
Given are $N$ strings $S_1,\ldots,S_N$ , each of which is AND or OR.
Find the number of tuples of $N+1$ variables $(x_0,\ldots,x_N)$ , where each element is $\text{True}$ or $\text{False}$ , such that the following computation results in $y_N$ being $\text{True}$ :
- $y_0=x_0$ ;
- for $i\geq 1$ , $y_i=y_{i-1} \land x_i$ if $S_i$ is
AND, and $y_i=y_{i-1} \lor x_i$ if $S_i$ isOR.
Here, a $\land$ b and a $\lor$ b are logical operators.
Constraints
- $1 \leq N \leq 60$
- $S_i$ is
ANDorOR.
Sample Input 1
2
AND
OR
Sample Output 1
5
解法一
比赛的时候写了个巨丑的记忆化递归,虽然过了但是并不是很满意,这里实际上很容易直接递推。
$dp[i][j]$ :前 $i$ 个元素使得 $y_i$ 为 $j$ 的个数(0 为 F,1 为 T)
$$ \begin{aligned} {S_i=\text{AND}}: \begin{cases} dp[i][0] = \underbrace{dp[i-1][0] + dp[i-1][1]}{x_i=false} + \underbrace{dp[i-1][0]}{x_i=true} \\ dp[i][1] = \underbrace{dp[i-1][1]}_{x_i=true} \end{cases} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} {S_i=\text{OR}}: \begin{cases} dp[i][0] = \underbrace{dp[i-1][0]}{x_i=false} \\ dp[i][1] = \underbrace{dp[i-1][1] + dp[i-1][0]}{x_i=true} + \underbrace{dp[i-1][1]}_{x_i=false} \end{cases} \end{aligned} $$
代码实现
//代码还可以进行空间降维,注意消除前后依赖就行了
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String... args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
//前 i 个元素,yi 为 F 和 T
long[][] dp = new long[N+1][2];
dp[0][0] = dp[0][1] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
String op = sc.next();
if ("AND".equals(op)) {
dp[i][1] = dp[i-1][1];
dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][1] + dp[i-1][0] + dp[i-1][0];
} else {
dp[i][1] = dp[i-1][0] + dp[i-1][1] + dp[i-1][1];
dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0];
}
}
System.out.println(dp[N][1]);
}
}
E - Rotate and Flip
There are $N$ pieces on a two-dimensional plane. The coordinates of Piece $i$ are $(X_i,Y_i)$ . There may be multiple pieces at the same coordinates.
We will do $M$ operations $\mathrm{op}_1, \ldots, \mathrm{op}_M$ , one by one. There are four kinds of operations, described below along with their formats in input.
1:Rotate every piece $90$ degrees clockwise about the origin;2:Rotate every piece $90$ degrees counterclockwise about the origin;3 p:Move each piece to the point symmetric to it about the line $x=p$ ;4 p:Move each piece to the point symmetric to it about the line $y=p$ .
You are given $Q$ queries. In the $i$ -th query, given two integers $A_i$ and $B_i$ , print the coordinates of Piece $B_i$ just after the $A_i$ -th operation. Here, the moment just before the $1$ -st operation is considered to be the moment just after “the $0$ -th operation”.
Constraints
- All values in input are integers.
- $1 \leq N \leq 2\times 10^5$
- $1 \leq M \leq 2\times 10^5$
- $1 \leq Q \leq 2\times 10^5$
- $10^9 \leq X_i,Y_i \leq 10^9$
- $\mathrm{op}_i$ is in the format of one of the four kinds of operations.
- In an operation with the form
3 por4 p, $-10^9 \leq p \leq 10^9$ . - $0 \leq A_i \leq M$
- $1 \leq B_i \leq N$
Sample Input 1
1
1 2
4
1
3 3
2
4 2
5
0 1
1 1
2 1
3 1
4 1
Sample Output 1
1 2
2 -1
4 -1
1 4
1 0
Initially, the only piece - Piece $1$ - is at $(1, 2)$ . Each operation moves the piece as follows: $(1,2)\to(2,-1)\to(4,-1)\to(1,4)\to(1,0)$ .
解法一
题目意思就是:给你 $N$ 个点,然后给你 $M$ 个操作(有序),然后给你 $Q$ 个查询,每个查询有两个值 $A_i$ 和 $B_i$ ,返回第 $B_i$ 个点在经过第 $A_i$ 次操作后的坐标
做法就是将所有的操作叠加起来,这里题目说了操作都是有序的,所以我们按顺序叠加 $M$ 个操作,然后针对每个查询我们就可以 $O(1)$ 的求出结果
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int N = readOne(br);
int[] x = new int[N];
int[] y = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
x[i] = t[0]; y[i] = t[1];
}
int M = readOne(br);
//将操作叠加起来
//1.(x, y) --> (y, -x)
//2.(x, y) --> (-y, x)
//3.(x, y) --> (-x+2p, y)
//4.(x, y) --> (x, -y+2p)
boolean[] swap = new boolean[M+1];
long[] addx = new long[M+1];
long[] addy = new long[M+1];
long[] mulx = new long[M+1];
long[] muly = new long[M+1];
mulx[0] = muly[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= M; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
if (t[0] == 1) {
swap[i] = !swap[i-1];
mulx[i] = muly[i-1]; muly[i] = -mulx[i-1];
addx[i] = addy[i-1]; addy[i] = -addx[i-1];
} else if (t[0] == 2) {
swap[i] = !swap[i-1];
mulx[i] = -muly[i-1]; muly[i] = mulx[i-1];
addx[i] = -addy[i-1]; addy[i] = addx[i-1];
} else if (t[0] == 3) {
swap[i] = swap[i-1];
mulx[i] = -mulx[i-1]; muly[i] = muly[i-1];
addx[i] = 2l*t[1] - addx[i-1]; addy[i] = addy[i-1];
} else if (t[0] == 4) {
swap[i] = swap[i-1];
mulx[i] = mulx[i-1]; muly[i] = -muly[i-1];
addx[i] = addx[i-1]; addy[i] = 2l*t[1] - addy[i-1];
}
}
int Q = readOne(br);
for (int i = 0; i < Q; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
int a = t[0], b = t[1]-1;
if (!swap[a]) {
out.println((x[b]*mulx[a] + addx[a]) + " " + (y[b]*muly[a] + addy[a]));
} else {
out.println((y[b]*mulx[a] + addx[a]) + " " + (x[b]*muly[a] + addy[a]));
}
}
out.flush();
out.close();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
public static int readOne(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
}
}
具体的 addx,addy,mulx… 这些参数的变化最好找一个例子自己代入试一下,空想容易搞错
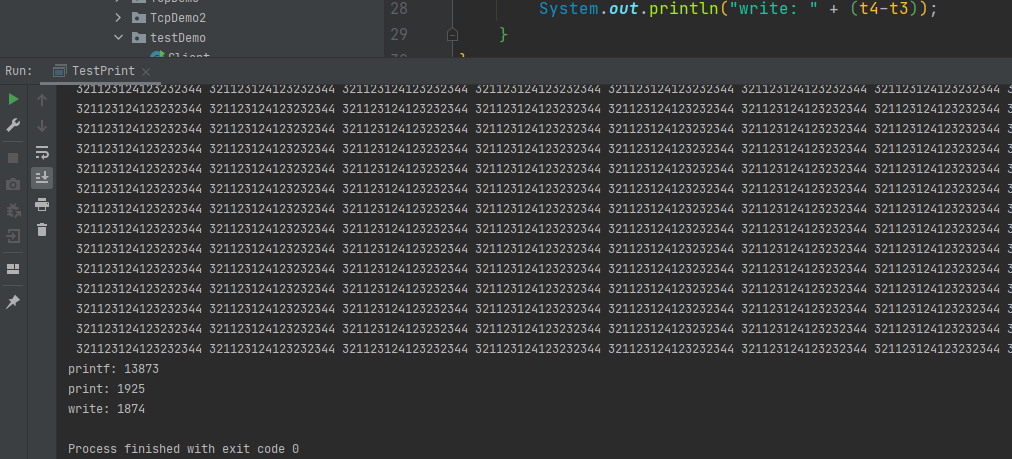
这里踩了个小坑,Java 的 prinf 效率会比 print 以及 write 慢很多,虽然可以想象到会慢一点,没想到会慢这么多,上面这题一开始用的 printf 打印的结果,然后就 T 了。.. 后面我自己测试了一下,发现确实会慢很多,以后要慎用了 TestCode
这题实际上还有一个利用矩阵的解法,相对来说会比较直接简单,官方题解也是用的矩阵的做法,后面有时间再来补充
F - Sugoroku2
暂时还没搞懂,后面再来补