搜索:0-1BFS
175. 电路维修
达达是来自异世界的魔女,她在漫无目的地四处漂流的时候,遇到了善良的少女翰翰,从而被收留在地球上。
翰翰的家里有一辆飞行车。
有一天飞行车的电路板突然出现了故障,导致无法启动。
电路板的整体结构是一个 $R$ 行 $C$ 列的网格 $(R,C≤500)$ ,如下图所示。
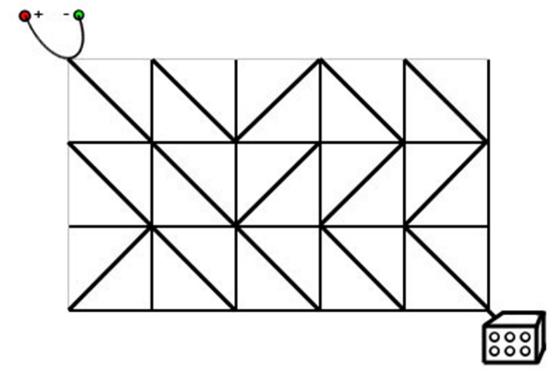
每个格点都是电线的接点,每个格子都包含一个电子元件。
电子元件的主要部分是一个可旋转的、连接一条对角线上的两个接点的短电缆。
在旋转之后,它就可以连接另一条对角线的两个接点。
电路板左上角的接点接入直流电源,右下角的接点接入飞行车的发动装置。
达达发现因为某些元件的方向不小心发生了改变,电路板可能处于断路的状态。
她准备通过计算,旋转最少数量的元件,使电源与发动装置通过若干条短缆相连。
不过,电路的规模实在是太大了,达达并不擅长编程,希望你能够帮她解决这个问题。
注意:只能走斜向的线段,水平和竖直线段不能走。
输入格式
输入文件包含多组测试数据。
第一行包含一个整数 $T$ ,表示测试数据的数目。
对于每组测试数据,第一行包含正整数 $R$ 和 $C$ ,表示电路板的行数和列数。
之后 $R$ 行,每行 $C$ 个字符,字符是"/“和”"中的一个,表示标准件的方向。
输出格式
对于每组测试数据,在单独的一行输出一个正整数,表示所需的缩小旋转次数。
如果无论怎样都不能使得电源和发动机之间连通,输出NO SOLUTION。
数据范围
- $1≤R,C≤500$
- $1≤T≤5$
输入样例:
1
3 5
\\/\\
\\///
/\\\\
输出样例:
1
解法一
题中元件连接的是对角线的两个节点,每一次流动横纵坐标都是同时加 1,同时减 1,或者一个加 1 一个减 1,而我们是从左上角第一个节点(0,0)开始,所以途径的点横纵坐标之和必然是偶数,奇数点是不可达的。所以可以对偶数点建图然后直接跑 Dijkstra 来求,但是这里有更好的处理方式「双端队列广搜(0-1BFS)」
通过偶数点建图时,如果两个点之间可以通过旋转元件连通,则权值为 1,如果不用旋转则权值为 0。图的权值只有 0 和 1,当 bfs 搜索的时候将权值为 0 的点加入队列头,权值为 1 的节点放到队尾,以此来保持单调性。这样队列头就是当前距离源点最近的点,出队列的时候标识已确定最短路,然后对出边进行松弛。
其实整体的思想和 Dijkstra 是一样的,只是实现的方式不一样。可以理解为对 Dijkstra 的优化,在边权值只有 0 和 1 的时候采用双端队列维护最短路的单调性,将时间复杂度优化到 $O(N)$
from collections import deque
T = int(input())
# 格点和斜线的方向向量,顺序要对应
d1 = [[-1, -1], [-1, 1], [1, 1], [1, -1]]
d2 = [[-1, -1], [-1, 0], [0, 0], [0, -1]]
chs = '\\/\\/'
while T > 0:
T = T - 1
r, c = map(int, input().split())
# 斜线
w = ['' for _ in range(r)]
# 格点
dis = [[float('inf') for _ in range(c + 1)] for _ in range(r + 1)]
vis = [[0 for _ in range(c + 1)] for _ in range(r + 1)]
for i in range(r):
w[i] = input()
if (r + c) & 1:
print('NO SOLUTION')
continue
q = deque()
q.append((0, 0))
dis[0][0] = 0
while q:
x, y = q.popleft()
if x == r and y == c:
break
if vis[x][y]:
continue
vis[x][y] = 1
# 遍历 4 个方向的格点
for i in range(4):
nx = x + d1[i][0]
ny = y + d1[i][1]
if nx < 0 or ny < 0 or nx >= r+1 or ny >= c+1:
continue
d = 0 if chs[i] == w[x + d2[i][0]][y + d2[i][1]] else 1
if dis[x][y] + d < dis[nx][ny]:
q.append((nx, ny)) if d else q.appendleft((nx, ny))
dis[nx][ny] = dis[x][y] + d
print(dis[r][c])
340. 通信线路
在郊区有 $N$ 座通信基站, $P$ 条 双向 电缆,第 $i$ 条电缆连接基站 $A_i$ 和 $B_i$ 。
特别地, $1$ 号基站是通信公司的总站, $N$ 号基站位于一座农场中。
现在,农场主希望对通信线路进行升级,其中升级第 $i$ 条电缆需要花费 $L_i$ 。
电话公司正在举行优惠活动。
农产主可以指定一条从 $1$ 号基站到 $N$ 号基站的路径,并指定路径上不超过 $K$ 条电缆,由电话公司免费提供升级服务。
农场主只需要支付在该路径上剩余的电缆中,升级价格最贵的那条电缆的花费即可。
求至少用多少钱可以完成升级。
输入格式
第 $1$ 行:三个整数 $N,P,K$ 。
第 $2..P+1$ 行:第 $i+1$ 行包含三个整数 $A_i,B_i,L_i$ 。
输出格式 包含一个整数表示最少花费。
若 $1$ 号基站与 $N$ 号基站之间不存在路径,则输出 $−1$ 。
数据范围
- $0≤K<N≤1000$
- $1≤P≤10000$
- $1≤L_i≤1000000$
输入样例:
5 7 1
1 2 5
3 1 4
2 4 8
3 2 3
5 2 9
3 4 7
4 5 6
输出样例:
4
解法一
原题是 [USACO08JAN]Telephone Lines S(洛谷似乎对 Java 不太友好,之前只是听说时间不放宽,但是我发现似乎连 Java8 的语法支持都不全,导致我的输入板子会直接 RE。但是在它的在线 IDE 里面又是正常的,放弃了放弃了)
这题题意再简化一下就是找到一条 $1$ 到 $N$ 的路径,求修建的最低费用。路径中有 $k$ 条是不用收费的,收费的是除了 $k$ 条路径之外,权值最高的那一条的修建费用。如果路径低于 $k$ 条显然就是完全免费了
这题要求的是一个最大最小值,所以我们可以直接二分修建费用 res。然后 check 在 res 的限制下能否找到一条路径 cover 住,check 的方法也很简单,我们把路径中大于 res 的路径看做权值为 $1$ 的边,反之则看做权值为 $0$ 的边。这里的权值为消耗免费路径的条数,所以大于 res 的我们就让它走免费线路消耗免费额度,反之则不走不消耗免费额度。然后我们就可以做一个 01-BFS,求出 1-N 的最短路,最后判断消耗的免费额度是否超过 $k$ 就行了。时间复杂度 $O(P\log{\max(L_i)})$
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
static int N;
static int P;
static int K;
static int[] A, B, L;
static int idx;
static int[] e, ne, h, w;
static Deque<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
static int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
static int[] dis;
//a->b
static void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b; w[idx] = c;
ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx++;
}
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int[] in = read(br);
N = in[0]; P = in[1]; K = in[2];
L = new int[P+1]; A = new int[P+1]; B = new int[P+1];
e = new int[2*P+1]; ne = new int[2*P+1]; w = new int[2*P+1]; h = new int[N+1];
for (int i = 0; i < P; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
A[i] = t[0]; B[i] = t[1]; L[i] = t[2];
}
int left = 0, right = 1000000;
int res = -1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right-left)/2;
if (bfs(mid)) {
res = mid;
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
out.println(res);
out.flush();
}
public static boolean bfs(int cost) {
queue.clear();
idx = 0;
Arrays.fill(e, 0);
Arrays.fill(w, 0);
Arrays.fill(ne, 0);
Arrays.fill(h, -1);
dis = new int[N+1];
Arrays.fill(dis, INF);
for (int i = 0; i < P; i++) {
// 大于 cost 的不付钱,算在免费的 K 条电缆中,消耗免费额度,权值为 1
// 小于等于 cost 的部分付 cost,不算在免费额度中,权值为 0(权值为消耗免费额度的数量,最后判断最短路能否小于 k)
add(A[i], B[i], (L[i] > cost) ? 1 : 0);
add(B[i], A[i], (L[i] > cost) ? 1 : 0);
}
queue.add(1);
dis[1] = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int i = queue.pop();
for (int j = h[i]; j != -1; j = ne[j]) {
if (dis[e[j]] > dis[i] + w[j]) {
dis[e[j]] = dis[i] + w[j];
if (w[j] == 0) {
queue.addFirst(e[j]);
} else {
queue.add(e[j]);
}
}
}
}
//System.out.printf("cost = %d, dis[N] = %d \n", cost, dis[N]);
return dis[N] <= K;
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
这题似乎还有别的做法,以后再来研究
1368. 使网格图至少有一条有效路径的最小代价
Difficulty: 困难
给你一个 m x n 的网格图 grid 。 grid 中每个格子都有一个数字,对应着从该格子出发下一步走的方向。 grid[i][j] 中的数字可能为以下几种情况:
- 1 ,下一步往右走,也就是你会从
grid[i][j]走到grid[i][j + 1] - 2 ,下一步往左走,也就是你会从
grid[i][j]走到grid[i][j - 1] - 3 ,下一步往下走,也就是你会从
grid[i][j]走到grid[i + 1][j] - 4 ,下一步往上走,也就是你会从
grid[i][j]走到grid[i - 1][j]
注意网格图中可能会有 无效数字 ,因为它们可能指向 grid 以外的区域。
一开始,你会从最左上角的格子 (0,0) 出发。我们定义一条 有效路径 为从格子 (0,0) 出发,每一步都顺着数字对应方向走,最终在最右下角的格子 (m - 1, n - 1) 结束的路径。有效路径 不需要是最短路径 。
你可以花费 cost = 1 的代价修改一个格子中的数字,但每个格子中的数字 只能修改一次 。
请你返回让网格图至少有一条有效路径的最小代价。
示例 1:
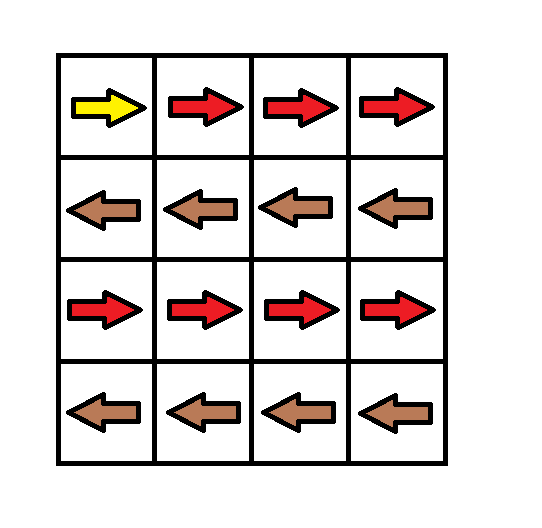
输入:grid = [[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2],[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2]]
输出:3
解释:你将从点 (0, 0) 出发。
到达 (3, 3) 的路径为: (0, 0) --> (0, 1) --> (0, 2) --> (0, 3) 花费代价 cost = 1 使方向向下 --> (1, 3) --> (1, 2) --> (1, 1) --> (1, 0) 花费代价 cost = 1 使方向向下 --> (2, 0) --> (2, 1) --> (2, 2) --> (2, 3) 花费代价 cost = 1 使方向向下 --> (3, 3)
总花费为 cost = 3.
示例 2:
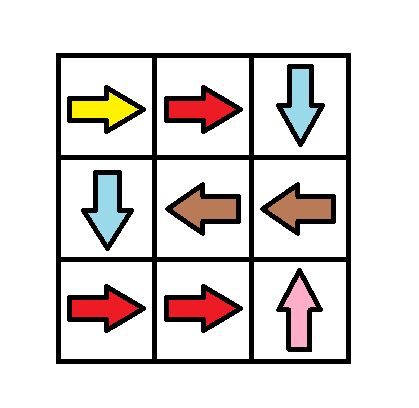
输入:grid = [[1,1,3],[3,2,2],[1,1,4]]
输出:0
解释:不修改任何数字你就可以从 (0, 0) 到达 (2, 2) 。
示例 3:
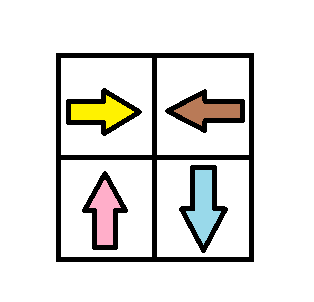
输入:grid = [[1,2],[4,3]]
输出:1
示例 4:
输入:grid = [[2,2,2],[2,2,2]]
输出:3
示例 5:
输入:grid = [[4]]
输出:0
提示:
- $\text{m = grid.length}$
- $\text{n = grid[i].length}$
- $1 \leq m, n \leq 100$
解法一
将修改次数作为权值,那么当前格点与箭头所指的相邻格点权值为 0,否则为 1,然后就成了典型的 0-1BFS,时间复杂度 $O(MN)$
from collections import deque
from typing import List
class Solution:
def minCost(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
# 顺序不能乱,1234 右左下上
dire = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]
n, m = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dis = [[float('inf') for _ in range(m+1)] for _ in range(n+1)]
vis = [[0 for _ in range(m+1)] for _ in range(n+1)]
q = deque()
q.append((0, 0))
dis[0][0] = 0
while q:
x, y = q.popleft()
if vis[x][y]:
continue
vis[x][y] = 1
for i in range(4):
nx, ny = x+dire[i][0], y+dire[i][1]
if nx < 0 or ny < 0 or nx >= n or ny >= m:
continue
w = 0 if (grid[x][y]-1) == i else 1
if dis[nx][ny] > dis[x][y] + w:
dis[nx][ny] = dis[x][y] + w
q.append((nx, ny)) if w else q.appendleft((nx, ny))
return dis[n-1][m-1]
这题其实还有个问题需要注意,题目中说了「每个格子中的数字只能修改一次」这个条件,但是实际上这对我们没有影响,经过第二次的修改次数肯定是大于等于第一次的。官方题解给出了证明,我不再赘述,上面 电路维修也有这个条件
CF1063B. Labyrinth
You are playing some computer game. One of its levels puts you in a maze consisting of $n$ lines, each of which contains $m$ cells. Each cell either is free or is occupied by an obstacle. The starting cell is in the row $r$ and column $c$ . In one step you can move one square up, left, down or right, if the target cell is not occupied by an obstacle. You can’t move beyond the boundaries of the labyrinth.
Unfortunately, your keyboard is about to break, so you can move left no more than $x$ times and move right no more than $y$ times. There are no restrictions on the number of moves up and down since the keys used to move up and down are in perfect condition.
Now you would like to determine for each cell whether there exists a sequence of moves that will put you from the starting cell to this particular one. How many cells of the board have this property?
Input
The first line contains two integers $n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 2000)$ — the number of rows and the number columns in the labyrinth respectively.
The second line contains two integers $r, c (1 ≤ r ≤ n, 1 ≤ c ≤ m)$ — index of the row and index of the column that define the starting cell.
The third line contains two integers $x, y (0 ≤ x, y ≤ 109)$ — the maximum allowed number of movements to the left and to the right respectively.
The next n lines describe the labyrinth. Each of them has length of m and consists only of symbols . and *. The $j$ -th character of the $i$ -th line corresponds to the cell of labyrinth at row $i$ and column $j$ . Symbol . denotes the free cell, while symbol * denotes the cell with an obstacle.
It is guaranteed, that the starting cell contains no obstacles.
Output
Print exactly one integer — the number of cells in the labyrinth, which are reachable from starting cell, including the starting cell itself.
Examples
4 5
3 2
1 2
.....
.***.
...**
*....
out
10
解法一
很容易写错的一道题,不细想很可能写出下面的代码
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int N, M;
static int R, C;
static int X, Y;
static int[][] grid;
static boolean[][] vis;
static int[][] remainX, remainY;
// 左右下上
static int[][] dir = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int[] nm = read(br);
N = nm[0]; M = nm[1];
int[] rc = read(br);
R = rc[0]; C = rc[1];
int[] xy = read(br);
X = xy[0]; Y = xy[1];
grid = new int[N][M];
vis = new boolean[N+1][M+1];
remainX = new int[N+1][M+1];
remainY = new int[N+1][M+1];
remainX[R][C] = X;
remainY[R][C] = Y;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
grid[i] = read0(br);
}
Deque<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(new int[]{R, C});
vis[R][C] = true;
int cnt = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = queue.poll();
int x = cur[0], y = cur[1];
cnt++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dir[i][0];
int ny = y + dir[i][1];
if ((i==0 && remainX[x][y]==0) || (i==1 && remainY[x][y]==0)) {
continue;
}
if (nx <= 0 || ny <= 0 || nx > N || ny > M || vis[nx][ny] || grid[nx-1][ny-1] == '*') {
continue;
}
queue.add(new int[]{nx, ny});
vis[nx][ny] = true;
remainX[nx][ny] = remainX[x][y] - (i==0 ? 1 : 0);
remainY[nx][ny] = remainY[x][y] - (i==1 ? 1 : 0);
}
}
out.println(cnt);
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
public static int[] read0(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split("")).mapToInt(c->(int)c.charAt(0)).toArray();
}
}
// public class CF1063B_Labyrinth {
// public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// new Main().main();
// }
// }
// }
但是上面忽略了一个很重要的问题,就是一个点可能会重复的到达,而到达的路径和方式不同消耗的左右步数也不同,很可能第一次到达该点时候消耗的左右步数并不是最少的,进而导致某些点可能明明可以到达但是漏掉了。
一个很容易想到的解决方法是在再次访问到某节点的时候保留消耗最小的数据,这样就不会漏掉。这里还有一种解决方案就是本文的重点「0-1BFS」,我们将纵向的移动看做权值为 0,将横向的移动看做权值为 1,然后求最短路。这样就能保证到每个节点的时候消耗都是最小的,最终能访问到的节点也是最多的
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class CF1063B_Labyrinth {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new Main().main();
}
}
class Main {
static int N, M;
static int R, C;
static int X, Y;
static int[][] grid;
static boolean[][] vis;
static int[][] remainX, remainY;
// 左右下上
static int[][] dir = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int[] nm = read(br);
N = nm[0]; M = nm[1];
int[] rc = read(br);
R = rc[0]; C = rc[1];
int[] xy = read(br);
X = xy[0]; Y = xy[1];
grid = new int[N][M];
vis = new boolean[N+1][M+1];
remainX = new int[N+1][M+1];
remainY = new int[N+1][M+1];
remainX[R][C] = X;
remainY[R][C] = Y;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
grid[i] = read0(br);
}
Deque<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(new int[]{R, C});
vis[R][C] = true;
int cnt = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = queue.poll();
int x = cur[0], y = cur[1];
cnt++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dir[i][0];
int ny = y + dir[i][1];
if ((i==0 && remainX[x][y]==0) || (i==1 && remainY[x][y]==0)) {
continue;
}
if (nx <= 0 || ny <= 0 || nx > N || ny > M || vis[nx][ny] || grid[nx-1][ny-1] == '*') {
continue;
}
if (i == 2 || i == 3) {
queue.addFirst(new int[]{nx, ny});
} else {
queue.add(new int[]{nx, ny});
}
vis[nx][ny] = true;
remainX[nx][ny] = remainX[x][y] - (i==0 ? 1 : 0);
remainY[nx][ny] = remainY[x][y] - (i==1 ? 1 : 0);
}
}
out.println(cnt);
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
public static int[] read0(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split("")).mapToInt(c->(int)c.charAt(0)).toArray();
}
}
CF173B. Chamber of Secrets
“The Chamber of Secrets has been opened again” — this news has spread all around Hogwarts and some of the students have been petrified due to seeing the basilisk. Dumbledore got fired and now Harry is trying to enter the Chamber of Secrets. These aren’t good news for Lord Voldemort. The problem is, he doesn’t want anybody to be able to enter the chamber. The Dark Lord is going to be busy sucking life out of Ginny.
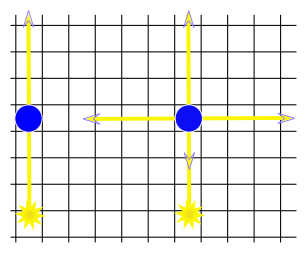
The Chamber of Secrets is an $n × m$ rectangular grid in which some of the cells are columns. A light ray (and a basilisk’s gaze) passes through the columns without changing its direction. But with some spell we can make a column magic to reflect the light ray (or the gaze) in all four directions when it receives the ray. This is shown in the figure below.
The basilisk is located at the right side of the lower right cell of the grid and is looking to the left (in the direction of the lower left cell). According to the legend, anyone who meets a basilisk’s gaze directly dies immediately. But if someone meets a basilisk’s gaze through a column, this person will get petrified. We know that the door to the Chamber is located on the left side of the upper left corner of the grid and anyone who wants to enter will look in the direction of its movement (in the direction of the upper right cell) from that position.
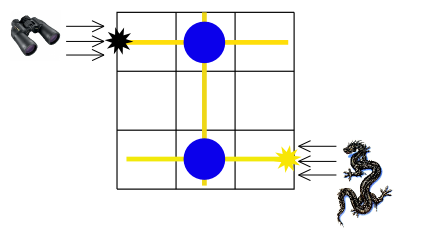
Given the dimensions of the chamber and the location of regular columns, Lord Voldemort has asked you to find the minimum number of columns that we need to make magic so that anyone who wants to enter the chamber would be petrified or just declare that it’s impossible to secure the chamber.
Input
The first line of the input contains two integer numbers n and m $(2 ≤ n, m ≤ 1000)$ . Each of the next $n$ lines contains $m$ characters. Each character is either “.” or “#” and represents one cell of the Chamber grid. It’s “.” if the corresponding cell is empty and “#” if it’s a regular column.
Output
Print the minimum number of columns to make magic or -1 if it’s impossible to do.
Examples
3 3
.#.
...
.#.
oUT
2
Note
The figure above shows the first sample test. In the first sample we should make both columns magic. The dragon figure represents the basilisk and the binoculars represent the person who will enter the Chamber of secrets. The black star shows the place where the person will be petrified. Yellow lines represent basilisk gaze moving through columns.
解法一
顺着「0-1BFS」搜索到的题,但是并没有写出对应的做法,这题「0-1BFS」并不是最优解,这题我 Java 用「0-1BFS」直接超时了。
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class CF173B_ChamberOfSecrets {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new Main().main();
}
}
class Main {
static int N, M;
static char[][] grid;
static boolean[][][] vis;
static int[][][] dis;
static int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
static int[][] dir = {{0, -1}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}};
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int[] nm = read(br);
N = nm[0]; M = nm[1];
grid = new char[N+1][M+1];
vis = new boolean[N+1][M+1][4];
dis = new int[N+1][M+1][4];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= M; j++) {
Arrays.fill(dis[i][j], INF);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
grid[i] = ("0"+br.readLine()).toCharArray();
}
Deque<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(new int[]{N, M, 0});
dis[N][M][0] = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = queue.poll();
int x = cur[0], y = cur[1], p = cur[2];
if (x == 1 && y == 1 && p == 0) break;
if (vis[x][y][p]) continue;
vis[x][y][p] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dir[i][0], ny = y + dir[i][1];
if (nx <= 0 || nx > N || ny <= 0 || ny > M) continue;
if (i == p) {
queue.addFirst(new int[]{nx, ny, p});
dis[nx][ny][i] = dis[x][y][p];
} else if (grid[x][y] == '#') {
if (dis[x][y][p] + 1 < dis[nx][ny][i]) {
dis[nx][ny][i] = dis[x][y][p] + 1;
queue.add(new int[]{nx, ny, i});
}
}
}
}
out.println(dis[1][1][0]==INF ? -1 : dis[1][1][0]);
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
解法二
也是我一开始想出来的解法,直接将行列看做点,横纵之间权值为 1。从最后一行开始,然后求第一行的最短路 $dis[1]$ 就行了,权值为 1 直接 BFS 就行了,应该是最优解,时间复杂度 $O(N+M)$
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class CF173B_ChamberOfSecrets {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new Main().main();
}
}
class Main {
static int N, M;
static char[][] grid;
static boolean[] vis;
static int[] dis;
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int[] nm = read(br);
N = nm[0]; M = nm[1];
grid = new char[N+1][M+1];
vis = new boolean[N+M+1];
dis = new int[N+M+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
grid[i] = ("0"+br.readLine()).toCharArray();
}
Deque<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(N);
vis[N] = true;
dis[N] = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int cur = queue.poll();
if (cur == 1) break;
if (cur <= N) { // 横向线条
for (int j = 1; j <= M; j++) {
if (!vis[j+N] && grid[cur][j] == '#') {
queue.add(j+N);
dis[j+N] = dis[cur] + 1;
vis[j+N] = true;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (!vis[i] && grid[i][cur-N] == '#') {
queue.add(i);
dis[i] = dis[cur] + 1;
vis[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
out.println(dis[1]==0 ? -1 : dis[1]);
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
翻了一下前排的做法,发现我的代码和 Petr 好像🤣