搜索:双向 BFS
双向奔赴的 BFS
190. 字串变换
已知有两个字串 $A, B$ 及一组字串变换的规则(至多 6 个规则):
$A1→B1$
$A2→B2$
…
规则的含义为:在 $A$ 中的子串 $A_1$ 可以变换为 $B_1$ 、 $A_2$ 可以变换为 $B_2$ …
例如:A=abcd B=xyz
变换规则为:
abc → xu ud → y y → yz
则此时,A 可以经过一系列的变换变为 B,其变换的过程为:
abcd → xud → xy → xyz
共进行了三次变换,使得 A 变换为 B。
输入格式:
A B
A1 B1
A2 B2
第一行是两个给定的字符串 A 和 B。
接下来若干行,每行描述一组字串变换的规则。
所有字符串长度的上限为 20。
输出格式
若在 10 步(包含 10 步)以内能将 A 变换为 B ,则输出最少的变换步数;否则输出 NO ANSWER!。
输入样例:
abcd xyz
abc xu
ud y
y yz
输出样例:
3
解法一
单看题面是一个简单的 BFS 搜索,但是分析下复杂度就会发现直接暴力代价是非常高的,最多会有 $6^{10}=60466176$ 状态,需要进行优化。
这里就引出「双向 BFS」的优化方法,我们平常 BFS 搜索是一个指数级别增长过程,每多搜索一层节点数量就会指数增长,那么我们肯定希望搜索的层数越少越好,那么我们就可采用「双向搜索」来优化。我们在进行原点->目标搜索的同时也进行目标->原点的搜索。

看上图好像只少了一点状态,实际我们稍微算一下就知道这个优化效果还是很明显的,假设每个节点可以扩展 $n$ 种状态,一共需要扩展 $k$ 层,那么可能(不算去重)就会有 $n^k$ 个状态。如果恰好搜索在中间相遇,那么我们的状态数量就会减少为 $n^{\frac{k}{2}}\ast2$ 。 对应到该题,实际上状态减少到了 $2\ast6^5=15552$ ,指数级别的大优化。当然双向 BFS 也并不是万能的,比如这题,如果数据量稍微再大一点,也会过不了,甚至也可以刻意的构造出在限制范围内双向 BFS 也无法通过的数据。
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
static int n;
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int ans = bfs(br);
out.println(ans == -1 ? "NO ANSWER!" : ans);
out.flush();
}
public static int bfs(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
String[] in = br.readLine().split(" ");
String A = in[0], B = in[1];
if (A.equals(B)) {
return 0;
}
// 正反搜索队列
Deque<String> qp = new ArrayDeque<>();
Deque<String> qn = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 正反搜索步数
HashMap<String, Integer> dp = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<String, Integer> dn = new HashMap<>();
// 转换规则
String[] sa = new String[7];
String[] sb = new String[7];
String line = null;
n = 0;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
String[] t = line.split(" ");
sa[n] = t[0]; sb[n++] = t[1];
}
qp.add(A); qn.add(B);
dp.put(A, 0); dn.put(B, 0);
int ans = -1, cnt = 0;
while (!qp.isEmpty() && !qn.isEmpty()) {
if (qp.size() < qn.size()) {
ans = expand(qp, dp, dn, sa, sb);
} else {
ans = expand(qn, dn, dp, sb, sa);
}
ans = expand(qp, dp, dn, sa, sb);
if (ans <= 10) return ans;
if (++cnt >= 10) return -1;
}
return -1;
}
public static int expand(Deque<String> que, Map<String, Integer> dp, Map<String, Integer> dn, String[] sa, String[] sb) {
int limit = dp.get(que.peek());
// 一次扩展一层
while (!que.isEmpty() && limit == dp.get(que.peek())) {
String cur = que.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 枚举规则
for (int j = 0, k = sa[i].length(); k <= cur.length(); j++, k++) { // 枚举字符
if (sa[i].equals(cur.substring(j, k))) {
String next = cur.substring(0, j) + sb[i] + cur.substring(k);
if (dn.containsKey(next)) {
return dp.get(cur) + 1 + dn.get(next);
}
// 去重
if (dp.containsKey(next)) continue;
dp.put(next, dp.get(cur) + 1);
que.add(next);
}
}
}
}
return 123456;
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
HDU-1195 Open the Lock
Now an emergent task for you is to open a password lock. The password is consisted of four digits. Each digit is numbered from $1$ to $9$ . Each time, you can add or minus 1 to any digit. When add 1 to ‘9’, the digit will change to be ‘1’ and when minus 1 to ‘1’, the digit will change to be ‘9’. You can also exchange the digit with its neighbor. Each action will take one step.
Now your task is to use minimal steps to open the lock.
Note: The leftmost digit is not the neighbor of the rightmost digit.
Input
The input file begins with an integer T, indicating the number of test cases.
Each test case begins with a four digit N, indicating the initial state of the password lock. Then followed a line with anotther four dight M, indicating the password which can open the lock. There is one blank line after each test case.
Output
For each test case, print the minimal steps in one line.
Sample Input
2
1234
2144
1111
9999
Sample Output
2
4
解法一
这题状态最多也就 $9^4$ ,其实完全不用双向 BFS,这里主要是为了练习。经过优化后时间减少了一半,还是很明显的。
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
static int[] d = {1, -1};
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int T = Integer.valueOf(br.readLine());
while (T-- > 0) {
String lock = br.readLine();
String pwd = br.readLine();
out.println(bfs(lock, pwd));
br.readLine(); // 空行
}
out.flush();
}
//11^4
public static int bfs(String lock, String pwd) {
HashMap<String, Integer> dz = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<String, Integer> df = new HashMap<>();
Deque<String> qz = new ArrayDeque<>();
Deque<String> qf = new ArrayDeque<>();
qz.add(lock); qf.add(pwd);
dz.put(lock, 0); df.put(pwd, 0);
int ans = -1;
while (!qz.isEmpty() && !qf.isEmpty()) {
if (qz.size() < qf.size()) {
ans = expand(qz, dz, df);
} else {
ans = expand(qf, df, dz);
}
if (ans != -1) break;
}
return ans;
}
public static int expand(Deque<String> que, HashMap<String, Integer> dz, HashMap<String, Integer> df) {
int step = dz.get(que.peek());
while (!que.isEmpty() && step == dz.get(que.peek())) {
char[] cs = que.poll().toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
change(cs, i, d[j]);
String next = new String(cs);
if (df.containsKey(next)) {
return df.get(next) + step + 1;
}
if (!dz.containsKey(next)) {
dz.put(next, step + 1);
que.add(next);
}
change(cs, i, -d[j]);
}
}
for (int i = 0, j = i+1; j < 4; i++, j++) {
swap(cs, i, j);
String next = new String(cs);
if (df.containsKey(next)) {
return df.get(next) + step + 1;
}
if (!dz.containsKey(next)) {
dz.put(next, step + 1);
que.add(next);
}
swap(cs, j, i);
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void change(char[] cs, int i, int d) {
if (cs[i] == '1' && d == -1) {
cs[i] = '9';
return;
}
if (cs[i] == '9' && d == 1) {
cs[i] = '1';
return;
}
cs[i] += d;
}
public static void swap(char[] cs, int a, int b) {
char t = cs[a];
cs[a] = cs[b];
cs[b] = t;
}
}
HDU-1401 Solitaire
Solitaire is a game played on a chessboard 8x8. The rows and columns of the chessboard are numbered from 1 to 8, from the top to the bottom and from left to right respectively.
There are four identical pieces on the board. In one move it is allowed to:
move a piece to an empty neighboring field (up, down, left or right),
jump over one neighboring piece to an empty field (up, down, left or right).
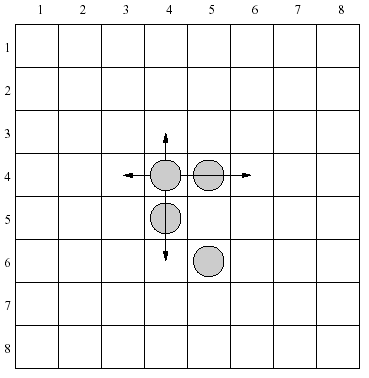
There are 4 moves allowed for each piece in the configuration shown above. As an example let’s consider a piece placed in the row 4, column 4. It can be moved one row up, two rows down, one column left or two columns right.
Write a program that:
reads two chessboard configurations from the standard input,
verifies whether the second one is reachable from the first one in at most 8 moves,
writes the result to the standard output.
解法一
同样,我们先分析暴力直接搜索的状态数量。4 个棋子,8x8 的棋盘,一共会有 $\tbinom{4}{64}$ 种状态,数量还是很大的。同时题目限制了最多走 8 步,也就是说可能会有 $16^8$ 个分支,大于状态数量,不仅会爆栈,时间也会超限。这里就可以采用「双向 BFS」优化。
我这里采用的「位压缩」来表示棋盘状态,用一个 long 长整形刚好。
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
static int[][] dir = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
// 64!
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null && !"".equals(line)) {
int[] as = toInts(line);
line = br.readLine();
int[] at = toInts(line);
long s = 0L, t = 0L;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i += 2) {
s = s | (1L << convert(as[i], as[i+1]));
t = t | (1L << convert(at[i], at[i+1]));
}
out.println(bfs(s, t) ? "YES" : "NO");
}
out.flush();
}
public static boolean bfs(long s, long t) {
Deque<Long> qz = new ArrayDeque<>(), qf = new ArrayDeque<>();
HashMap<Long, Integer> dz = new HashMap<>(), df = new HashMap<>();
qz.add(s); dz.put(s, 0);
qf.add(t); df.put(t, 0);
int ans = -1;
while (!qz.isEmpty() && !qf.isEmpty()) {
if (qz.size() <= qf.size()) {
ans = expand(qz, dz, df);
} else {
ans = expand(qf, df, dz);
}
if (ans > 8) return false;
if (ans >= 0) return true;
}
return false;
}
public static int expand(Deque<Long> que, HashMap<Long, Integer> dz, HashMap<Long, Integer> df) {
int step = dz.get(que.peek());
while (!que.isEmpty() && step == dz.get(que.peek())) {
long cur = que.poll();
long bak = cur;
int cnt = 0;
while (cur != 0) {
if ((cur&1) == 1) {
int x = cnt / 8 + 1;
int y = cnt % 8 + 1;
for (int[] d : dir) {
int nx = x + d[0];
int ny = y + d[1];
if (nx < 1 || nx > 8 || ny < 1 || ny > 8) {
continue;
}
if (((bak>>>convert(nx, ny)) & 1) == 1) {
int nnx = nx + d[0];
int nny = ny + d[1];
if (nnx < 1 || nnx > 8 || nny < 1 || nny > 8) {
continue;
}
if (((bak>>>convert(nnx, nny))&1)==1) {
continue;
}
nx = nnx; ny = nny;
}
long val = bak ^ (1L << cnt) | (1L << (convert(nx, ny)));
if (df.containsKey(val)) {
return df.get(val) + step + 1;
}
if (!dz.containsKey(val)) {
dz.put(val, step + 1);
que.add(val);
}
}
}
cur >>>= 1;
cnt++;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static int convert(int x, int y) {
return (x-1)*8 + y - 1;
}
public static int[] toInts(String str) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(str.split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
不太熟 HDOJ,看样例以为是单次输入,多次执行,谁知道它是一起输入的,还得自己判断结尾。在这里卡了好几天。.. 还是别人代码才发现,一直以为是自己代码有问题,吐了。