图论:单源最短路的建图方式
相关文章:图论:常见的最短路算法模板
1129. 热浪
德克萨斯纯朴的民众们这个夏天正在遭受巨大的热浪!!!
他们的德克萨斯长角牛吃起来不错,可是它们并不是很擅长生产富含奶油的乳制品,农夫 John 此时身先士卒地承担起向德克萨斯运送大量的营养冰凉的牛奶的重任,以减轻德克萨斯人忍受酷暑的痛苦。
John 已经研究过可以把牛奶从威斯康星运送到德克萨斯州的路线。这些路线包括起始点和终点一共有 $T$ 个城镇,为了方便标号为 $1$ 到 $T$ 。除了起点和终点外的每个城镇都由双向道路连向至少两个其它的城镇。每条道路有一个通过费用(包括油费,过路费等等)。
给定一个地图,包含 $C$ 条直接连接 2 个城镇的道路。每条道路由道路的起点 $R_s$ ,终点 $R_e$ 和花费 $C_i$ 组成。求从起始的城镇 $T_s$ 到终点的城镇 $T_e$ 最小的总费用。
输入格式
第一行:4 个由空格隔开的整数: $T,C,T_s,T_e$ ;
第 2 到第 $C+1$ 行:第 $i+1$ 行描述第 $i$ 条道路,包含 3 个由空格隔开的整数: $R_s,R_e,C_i$ 。
输出格式
一个单独的整数表示从 $T_s$ 到 $T_e$ 的最小总费用。数据保证至少存在一条道路。
数据范围
- $1≤T≤2500$
- $1≤C≤6200$
- $1≤Ts,Te,Rs,Re≤T$
- $1≤Ci≤1000$
输入样例:
7 11 5 4
2 4 2
1 4 3
7 2 2
3 4 3
5 7 5
7 3 3
6 1 1
6 3 4
2 4 3
5 6 3
7 2 1
输出样例:
7
解法一
很裸的题,正权图,数据范围不是很大,直接使用堆优化的Dijkstra
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int[] in = read(br);
int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int T = in[0], C = in[1], Ts = in[2], Te = in[3];
int[][] w = new int[T+1][T+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= T; i++) {
Arrays.fill(w[i], INF);
}
for (int i = 0; i < C; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
int x = t[0], y = t[1];
w[x][y] = Math.min(w[x][y], t[2]);
w[y][x] = Math.min(w[y][x], t[2]);
}
int[] dis = new int[T+1];
Arrays.fill(dis, INF);
dis[Ts] = 0;
boolean[] vis = new boolean[T+1];
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b)->dis[a]-dis[b]);
queue.add(Ts);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int i = queue.poll();
if (vis[i]) continue;
vis[i] = true;
for (int j = 1; j <= T; j++) {
if (w[i][j] == INF) continue;
if (dis[j] > dis[i] + w[i][j]) {
dis[j] = dis[i] + w[i][j];
queue.add(j);
}
}
}
out.println(dis[Te]);
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
1128. 信使
战争时期,前线有 $n$ 个哨所,每个哨所可能会与其他若干个哨所之间有通信联系。
信使负责在哨所之间传递信息,当然,这是要花费一定时间的(以天为单位)。 指挥部设在第一个哨所,当指挥部下达一个命令后,指挥部就派出若干个信使向与指挥部相连的哨所送信,当一个哨所接到信后,这个哨所内的信使们也以同样的方式向其他哨所送信。信在一个哨所内停留的时间可以忽略不计,直至所有 n 个哨所全部接到命令后,送信才算成功。
因为准备充足,每个哨所内都安排了足够的信使(如果一个哨所与其他 k 个哨所有通信联系的话,这个哨所内至少会配备 k 个信使)。
现在总指挥请你编一个程序,计算出完成整个送信过程最短需要多少时间。
输入格式
第 $1$ 行有两个整数 $n$ 和 $m$ ,中间用 $1$ 个空格隔开,分别表示有 $n$ 个哨所和 $m$ 条通信线路。
第 $2$ 至 $m+1$ 行:每行三个整数 $i,j,k$ ,中间用 $1$ 个空格隔开,表示第 $i$ 个和第 $j$ 个哨所之间存在 双向 通信线路,且这条线路要花费 $k$ 天。
输出格式
一个整数,表示完成整个送信过程的最短时间,如果不是所有的哨所都能收到信,就输出-1。
数据范围
- $1≤n≤100$
- $1≤m≤200$
- $1≤k≤1000$
输入样例:
4 4
1 2 4
2 3 7
2 4 1
3 4 6
输出样例:
11
解法一
求至少需要多长时间其实就是求最长的最短路,数据范围很小,可以直接 Floyd,我这里写了个 SPFA
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int[] in = read(br);
int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int N = in[0], M = in[1];
int[][] w = new int[N+1][N+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
Arrays.fill(w[i], INF);
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
int x = t[0], y = t[1];
w[x][y] = Math.min(w[x][y], t[2]);
w[y][x] = Math.min(w[y][x], t[2]);
}
int[] dis = new int[N+1];
boolean[] vis = new boolean[N+1];
Arrays.fill(dis, INF);
dis[1] = 0;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(1); vis[1] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int i = queue.poll();
vis[i] = false;
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
if (w[i][j]==INF) continue; //其实 dis[i] 不会为 INF
if (dis[j] > dis[i] + w[i][j]) {
dis[j] = dis[i] + w[i][j];
if (!vis[j]) {
queue.add(j);
vis[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
res = Math.max(res, dis[i]);
}
out.println(res==INF ? -1 : res);
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
1127. 香甜的黄油
农夫 John 发现了做出全威斯康辛州最甜的黄油的方法:糖。
把糖放在一片牧场上,他知道 $N$ 只奶牛会过来舔它,这样就能做出能卖好价钱的超甜黄油。当然,他将付出额外的费用在奶牛上。
农夫 John 很狡猾,就像以前的巴甫洛夫,他知道他可以训练这些奶牛,让它们在听到铃声时去一个特定的牧场。
他打算将糖放在那里然后下午发出铃声,以至他可以在晚上挤奶。
农夫 John 知道每只奶牛都在各自喜欢的牧场(一个牧场不一定只有一头牛)。
给出各头牛在的牧场和牧场间的路线,找出使所有牛到达的路程和最短的牧场(他将把糖放在那)。
数据保证至少存在一个牧场和所有牛所在的牧场连通。
输入格式
第一行:三个数:奶牛数 $N$ ,牧场数 $P$ ,牧场间道路数 $C$ 。
第二行到第 $N+1$ 行: $1$ 到 $N$ 头奶牛所在的牧场号。
第 $N+2$ 行到第 $N+C+1$ 行:每行有三个数:相连的牧场 $A,B$ ,两牧场间距 $D$ ,当然,连接是双向的。
输出格式
共一行,输出奶牛必须行走的最小的距离和。
数据范围
- $1≤N≤500$
- $2≤P≤800$
- $1≤C≤1450$
- $1≤D≤255$
输入样例:
3 4 5
2
3
4
1 2 1
1 3 5
2 3 7
2 4 3
3 4 5
输出样例:
8
解法一
单看题目,Floyd 肯定是比较契合的,直接求出任意两点的最短路,然后枚举所有的点,但是时间复杂度不合适,所以考虑使用堆优化的 Dijkstra,尝试以每个牧场作为源点,跑一遍最短路,然后求所有奶牛到该点的距离和,最终求一个最小的距离和,时间复杂度 $O(NM\log N)$
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
static int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
static int N, P, C;
static int[] cow;
static int[] e, h, ne, w;
static int idx;
//a->b
public static void add(int a, int b, int c) {
w[idx] = c; e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx++;
}
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int[] in = read(br);
N = in[0]; P = in[1]; C = in[2];
//边数:2*C
e = new int[C*2+1]; ne = new int[C*2+1]; w = new int[C*2+1];
//点数:P
h = new int[P+1]; Arrays.fill(h, -1);
cow = new int[N+1]; // 奶牛所在牧场
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
cow[i] = read(br)[0];
}
for (int i = 0; i < C; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
add(t[0], t[1], t[2]);
add(t[1], t[0], t[2]);
}
int res = INF;
for (int i = 1; i <= P; i++) {
res = Math.min(dijkstra(i), res);
}
out.println(res);
out.flush();
}
public static int dijkstra(int s) {
int[] dis = new int[P+1];
boolean[] vis = new boolean[P+1];
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->dis[a]-dis[b]);
Arrays.fill(dis, INF);
dis[s] = 0; pq.add(s);
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int i = pq.poll();
if (vis[i]) continue;
vis[i] = true;
for (int j = h[i]; j != -1; j = ne[j]) { //边编号
int k = e[j]; //点编号
if (w[j] == INF || dis[i] == INF) continue;
if (dis[k] > dis[i] + w[j]) {
dis[k] = dis[i] + w[j];
pq.add(k);
}
}
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (dis[cow[i]] == INF) return INF;
sum += dis[cow[i]];
}
return sum;
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
1126. 最小花费
在 $n$ 个人中,某些人的银行账号之间可以互相转账,这些人之间转账的手续费各不相同。
给定这些人之间转账时需要从转账金额里扣除百分之几的手续费,请问 $A$ 最少需要多少钱使得转账后 $B$ 收到 $100$ 元。
输入格式
第一行输入两个正整数 $n,m$ ,分别表示总人数和可以互相转账的人的对数。
以下 $m$ 行每行输入三个正整数 $x,y,z$ ,表示标号为 $x$ 的人和标号为 $y$ 的人之间互相转账需要扣除 $z%$ 的手续费 ( $z<100$ )。
最后一行输入两个正整数 $A,B$ 。
数据保证 $A$ 与 $B$ 之间可以直接或间接地转账。
输出格式
输出 $A$ 使得 $B$ 到账 $100$ 元最少需要的总费用。
精确到小数点后 $8$ 位。
数据范围
- $1≤n≤2000$
- $m≤105$
输入样例:
3 3
1 2 1
2 3 2
1 3 3
1 3
输出样例:
103.07153164
解法一
这题让我对最短路的概念有了新的理解,前面的题目都是求权值和最小的路径,而这题中我们的边权值 $w_i$ 是一个手续费的百分比数,我们设 $A$ 转出的金额为 $m$ ,根据题意可得 $m(1-w_1)(1-w_2)…(1-w_k)=100$ ,我们希望 $m$ 最小,也就是希望 $(1-w_1)(1-w_2)…(1-w_k)$ 越大,那么这里就变成了一个求乘法最长路的问题
我们知道 Dijkstra 核心思想是:每次从未确定的最短路集合中选取最短的一个,从而确定该点的最短路,然后利用该点去松弛其他的点,然后重复该过程。而这题中边的权值 $w_i$ 是一个小于 $1$ 的小数(大于 $0$ ),所以路径累乘是递减的,那么我们从未确定的乘法最长路集合中选取一个最大的点,它也就无法通过其他未确定的点中转来增大路径积,进而便可以确定该点的乘法最长路,符合 Dijkstara 的思想,所以该题可以直接使用 Dijkstra。
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
static int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
static int N, M;
static int idx;
static int[] e, ne, h, w;
//a->b
public static void add(int a, int b, int c){
e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a];
w[idx] = c; h[a] = idx++;
}
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int[] in = read(br);
int N = in[0], M = in[1];
e = new int[2*M+1]; ne = new int[2*M+1]; w = new int[2*M+1];
h = new int[N+1]; Arrays.fill(h, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
add(t[0], t[1], 100-t[2]);
add(t[1], t[0], 100-t[2]);
}
int[] t = read(br);
int A = t[0], B = t[1];
double[] dis = new double[N+1];
boolean[] vis = new boolean[N+1];
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->(dis[b]>dis[a])?1:-1);
dis[A] = 1.0; pq.add(A);
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int i = pq.poll();
if (vis[i]) continue;
vis[i] = true;
for (int j = h[i]; j != -1; j = ne[j]) {
int k = e[j];
if (dis[k] < dis[i] * (w[j]/100.0)) {
dis[k] = dis[i] * (w[j]/100.0);
pq.add(k);
}
}
}
out.printf("%.8f", 100/dis[B]);
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
进一步思考,如果权值都大于 $1$ ,显然我们就只能通过 Dijkstra 求乘法最短路,那么如果权值既有大于 1 的也有小于 1 的(大于 0)就只能用 SPFA 类似的算法了,并且 SPFA 既可以求最大值也能求最小值。
920. 最优乘车
$H$ 城是一个旅游胜地,每年都有成千上万的人前来观光。为方便游客,巴士公司在各个旅游景点及宾馆,饭店等地都设置了巴士站并开通了一些单程巴士线路。
每条单程巴士线路从某个巴士站出发,依次途经若干个巴士站,最终到达终点巴士站。
一名旅客最近到 $H$ 城旅游,他很想去 $S$ 公园游玩,但如果从他所在的饭店没有一路巴士可以直接到达 $S$ 公园,则他可能要先乘某一路巴士坐几站,再下来换乘同一站台的另一路巴士,这样换乘几次后到达 $S$ 公园。
现在用整数 $1,2,…N$ 给 $H$ 城的所有的巴士站编号,约定这名旅客所在饭店的巴士站编号为 $1,S$ 公园巴士站的编号为 $N$ 。
写一个程序,帮助这名旅客寻找一个最优乘车方案,使他在从饭店乘车到 $S$ 公园的过程中换乘的次数最少。
输入格式
第一行有两个数字 M 和 N,表示开通了 M 条单程巴士线路,总共有 N 个车站。
从第二行到第 M+1 行依次给出了第 1 条到第 M 条巴士线路的信息,其中第 i+1 行给出的是第 i 条巴士线路的信息,从左至右按运行顺序依次给出了该线路上的所有站号,相邻两个站号之间用一个空格隔开。
输出格式
共一行,如果无法乘巴士从饭店到达 S 公园,则输出 NO,否则输出最少换乘次数,换乘次数为 0 表示不需换车即可到达。
数据范围
- $1≤M≤100$
- $1≤N≤500$
输入样例:
3 7
6 7
4 7 3 6
2 1 3 5
输出样例:
2
解法一
关键点是如何建图,我一开始想了一个很复杂的的建图方式,然后发现太复杂了,就放弃了。这里其实直接将同一条路线的站点,从左到右任意两点用权值为 $1$ 的边进行连接就行了,然后跑一下最短路最后得到的答案减一就是最少换乘次数,算法瓶颈在建图上,时间复杂度 $O(MN^2)$
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
static int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
static int N, M;
static int[][] w;
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int[] in = read(br);
M = in[0]; N = in[1];
w = new int[N+1][N+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
Arrays.fill(w[i], INF);
}
//M*N*N
for (int i = 1; i <= M; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
for (int j = 0; j < t.length; j++) {
for (int k = j+1; k < t.length; k++) {
w[t[j]][t[k]] = 1;
}
}
}
int[] dis = new int[N+1];
boolean[] vis = new boolean[N+1];
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->dis[a]-dis[b]);
Arrays.fill(dis, INF);
dis[1] = 0; pq.add(1);
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int i = pq.poll();
if (vis[i]) continue;
vis[i] = true;
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
if (w[i][j] == INF) continue;
if (dis[j] > dis[i] + w[i][j]) {
dis[j] = dis[i] + w[i][j];
pq.add(j);
}
}
}
out.println(dis[N]==INF ? "NO" : dis[N]-1);
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
边权值为 $1$ ,其实直接 BFS 就可以了
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
static int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
static int N, M;
static int[][] w;
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int[] in = read(br);
M = in[0]; N = in[1];
w = new int[N+1][N+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
Arrays.fill(w[i], INF);
}
//M*N*N
for (int i = 1; i <= M; i++) {
int[] t = read(br);
for (int j = 0; j < t.length; j++) {
for (int k = j+1; k < t.length; k++) {
w[t[j]][t[k]] = 1;
}
}
}
int[] dis = new int[N+1];
Arrays.fill(dis, INF);
boolean[] vis = new boolean[N+1];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
dis[1] = 0; queue.add(1);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int i = queue.poll();
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
if (w[i][j] == INF || dis[j] != INF) continue;
dis[j] = dis[i] + w[i][j];
queue.add(j);
}
}
out.println(dis[N]==INF ? "NO" : dis[N]-1);
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
903. 昂贵的聘礼
年轻的探险家来到了一个印第安部落里。在那里他和酋长的女儿相爱了,于是便向酋长去求亲。酋长要他用 $10000$ 个金币作为聘礼才答应把女儿嫁给他。
探险家拿不出这么多金币,便请求酋长降低要求。
酋长说:”嗯,如果你能够替我弄到大祭司的皮袄,我可以只要 8000 金币。如果你能够弄来他的水晶球,那么只要 5000 金币就行了。”
探险家就跑到大祭司那里,向他要求皮袄或水晶球,大祭司要他用金币来换,或者替他弄来其他的东西,他可以降低价格。
探险家于是又跑到其他地方,其他人也提出了类似的要求,或者直接用金币换,或者找到其他东西就可以降低价格。
不过探险家没必要用多样东西去换一样东西,因为不会得到更低的价格。
探险家现在很需要你的帮忙,让他用最少的金币娶到自己的心上人。
另外他要告诉你的是,在这个部落里,等级观念十分森严。地位差距超过一定限制的两个人之间不会进行任何形式的直接接触,包括交易。他是一个外来人,所以可以不受这些限制。
但是如果他和某个地位较低的人进行了交易,地位较高的的人不会再和他交易,他们认为这样等于是间接接触,反过来也一样。
因此你需要在考虑所有的情况以后给他提供一个最好的方案。
为了方便起见,我们把所有的物品从 $1$ 开始进行编号,酋长的允诺也看作一个物品,并且编号总是 $1$ 。
每个物品都有对应的价格 $P$ ,主人的地位等级 $L$ ,以及一系列的替代品 $T_i$ 和该替代品所对应的”优惠” $V_i$ 。
如果两人地位等级差距超过了 $M$ ,就不能”间接交易”。
你必须根据这些数据来计算出探险家最少需要多少金币才能娶到酋长的女儿。
输入格式
输入第一行是两个整数 $M,N$ 依次表示地位等级差距限制和物品的总数。
接下来按照编号从小到大依次给出了 $N$ 个物品的描述。
每个物品的描述开头是三个非负整数 $P、L、X$ ,依次表示该物品的价格、主人的地位等级和替代品总数。
接下来 $X$ 行每行包括两个整数 $T$ 和 $V$ ,分别表示替代品的编号和”优惠价格”。
输出格式
输出最少需要的金币数。
数据范围
- $1≤N≤100$
- $1≤P≤10000$
- $1≤L,M≤N$
- $0≤X<N$
输入格式
1 4
10000 3 2
2 8000
3 5000
1000 2 1
4 200
3000 2 1
4 200
50 2 0
输出格式
5250
解法一
之前的解法有问题,被 Hack 了。
package main
import (
"bufio"
"container/heap"
"fmt"
"os"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
var price []int
var rank []int
var w [][]int
var INF = int(0x3f3f3f3f)
func main() {
// f, _ := os.Open("./input.txt")
// reader := bufio.NewReader(f)
reader := bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
// writer := bufio.NewWriter(os.Stdout)
t := ReadArray(reader)
M, N := t[0], t[1]
rank = make([]int, N+1)
w = make([][]int, N+1)
for i := 0; i <= N; i++ {
w[i] = make([]int, N+1)
for j := 0; j <= N; j++ {
w[i][j] = INF
}
}
for i := 1; i <= N; i++ {
plx := ReadArray(reader)
rank[i] = plx[1]
// 虚拟源点,连接所有节点
w[0][i] = plx[0]
for j := 0; j < plx[2]; j++ {
tv := ReadArray(reader)
// 反向建边
w[tv[0]][i] = tv[1]
}
}
var res = INF
// 枚举区间 [rank[1]-m, rank[1]+m]
for i := rank[1] - M; i <= rank[1]; i++ {
res = Min(res, Dijkstra(N, i, i+M))
}
fmt.Println(res)
}
func Dijkstra(n int, lt int, rt int) int {
pq := make(NodeHeap, 0)
vis := make([]bool, n+1)
dis := make([]int, n+1)
for i := 0; i <= n; i++ {
dis[i] = INF
}
heap.Push(&pq, &Node{
idx: 0,
val: 0,
})
dis[0] = 0
for len(pq) > 0 {
cur := heap.Pop(&pq).(*Node)
i, v := cur.idx, cur.val
if vis[i] {
continue
}
vis[i] = true
for j := 1; j <= n; j++ {
if rank[j] > rt || rank[j] < lt {
continue
}
if w[i][j] == INF {
continue
}
if w[i][j]+v < dis[j] {
dis[j] = w[i][j] + v
heap.Push(&pq, &Node{j, dis[j]})
}
}
}
return dis[1]
}
func Min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}
type Node struct {
idx int
val int
}
type NodeHeap []*Node
func (h NodeHeap) Len() int { return len(h) }
// 小顶堆
func (h NodeHeap) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].val < h[j].val }
func (h NodeHeap) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *NodeHeap) Push(x interface{}) {
// Push 和 Pop 使用 pointer receiver 作为参数,
// 因为它们不仅会对切片的内容进行调整,还会修改切片的长度。
*h = append(*h, x.(*Node))
}
func (h *NodeHeap) Pop() interface{} {
old := *h
n := len(old)
x := old[n-1]
*h = old[0 : n-1]
return x
}
func ReadLine(reader *bufio.Reader) string {
line, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')
return strings.TrimRight(line, "\n")
}
func ReadInt(reader *bufio.Reader) int {
num, _ := strconv.Atoi(ReadLine(reader))
return num
}
func ReadArray(reader *bufio.Reader) []int {
line := ReadLine(reader)
strs := strings.Split(line, " ")
nums := make([]int, len(strs))
for i, s := range strs {
nums[i], _ = strconv.Atoi(s)
}
return nums
}
错误解法示例
建图的时候直接建立当前物品和其替代品的边。记录每个物品的价格 $price$ 和主人等级 $rank$
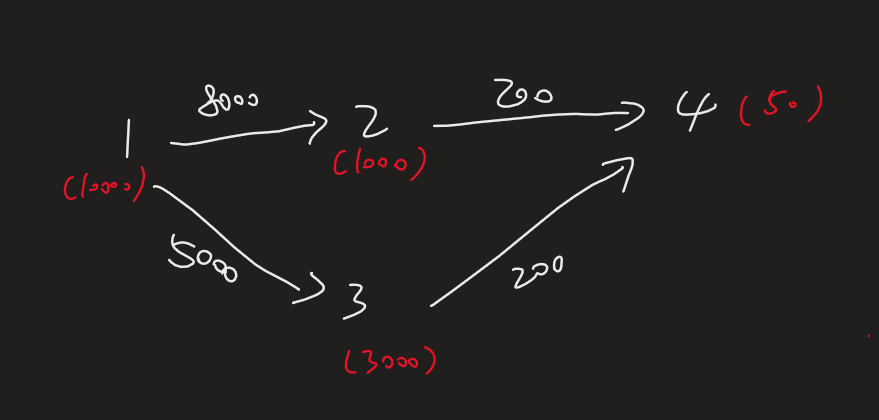
优先队列中存储节点的编号 $i$ ,当前离物品 $1$ (公主)的最短路 $v$ ,以及路径上的最大等级 $max$ 和最小等级 $min$ ,在松弛的时候判断等级有没有超过限制,并且维护这两个值,然后在优先队列弹出节点的时候统计最小值(弹出节点的最短路已经确定了,尝试在当前节点停止替换操作,直接原价购买)
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
static class Node {
int i, v;
int max, min;
public Node(int i, int v, int max, int min) {
this.i = i; this.v = v;
this.max = max; this.min = min;
}
}
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(System.out));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("./input.txt")));
int[] in = read(br);
int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int M = in[0], N = in[1];
int[][] w = new int[N+1][N+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
Arrays.fill(w[i], INF);
}
// 记录每个物品的价格和主人等级
int[] price = new int[N+1];
int[] rank = new int[N+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
int[] plx = read(br);
price[i] = plx[0]; rank[i] = plx[1];
for (int j = 1; j <= plx[2]; j++) {
int[] tv = read(br);
w[i][tv[0]] = tv[1];
}
}
int res = INF;
int[] dis = new int[N+1];
boolean[] vis = new boolean[N+1];
// pq 中存储节点的编号,以及路径上的最大和最小等级
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->a.v-b.v);
Arrays.fill(dis, INF);
dis[1] = 0; pq.add(new Node(1, 0, rank[1], rank[1]));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node node = pq.poll();
int i = node.i, v = node.v;
if (vis[i]) continue;
vis[i] = true;
// 在当前位置停止替换
res = Math.min(res, dis[i]+price[i]);
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
if (w[i][j] == INF) continue;
// 等级限制无法交易
if (Math.abs(rank[j]-node.min) > M ||
Math.abs(rank[j]-node.max) > M ) continue;
if (dis[j] > v + w[i][j]) {
dis[j] = v + w[i][j];
pq.add(new Node(j, dis[j], Math.max(rank[j], node.max), Math.min(rank[j], node.min)));
}
}
}
out.println(res);
out.flush();
}
public static int[] read(BufferedReader br) throws Exception {
return Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
}
这里我写完后看了下题解,发现和 y 总的做法不一样,y 总建图是反向建的,同时增加了虚拟节点指向单个的物品,然后枚举等级限制内的所有区间,在每个区间内跑一次最短路,最后求一个最小 $dis[1]$
一度以为是自己出了问题,去 POJ 上交了一下发现也是可以 AC 的
嗯,确实是自己出了问题。这里的解法是错的,每个节点可能在多条路径上,所以这里统计路径上的最大最小 rank 是不准确的,每个点都可能被松弛多次,并不能保证维护的一定是最短路上的 max,min(这个解法修改一下可以正确的 AC,但是感觉有点怪,就不再记录了,具体 参考)